

# 7 101541 Judson College private Marion AL Southeast # 6 101480 Jacksonville State University public Jacksonville AL Southeast
# 5 101453 Heritage Christian University private Florence AL Southeast # 4 101435 Huntingdon College private Montgomery AL Southeast # 3 101189 Faulkner University private Montgomery AL Southeast # 2 101073 Concordia College Alabama private Selma AL Southeast # 1 100937 Birmingham Southern College private Birmingham AL Southeast slice(colleges, 10: 16) # unitid college type city state region To extract rows 10 through 16 from the colleges data frame we use the slice function. How many private Maryland colleges with under 5000 undergraduates are in the colleges data frame?.How many Maryland colleges are in the colleges data frame? (The abbreviation for Maryland is MD.).Will eliminate only rows with NA in the cost column. ```Ĭolleges <- filter(colleges, !is.na(cost)) Will reduce the data set to only rows with no missing values. To remove rows with missing values, use the R command na.omit. For example, we can extract the colleges in Wisconsin from the colleges data set using the following code: wi, >=, <, <=, != (not equal), and = (equal). To extract the rows only for colleges and universities in a specific state we use the filter function. # admissionRate ACTmath ACTenglish undergrads cost gradRate FYretention # 6 100751 The University of Alabama public Tuscaloosa AL Southeast # 5 100724 Alabama State University public Montgomery AL Southeast # 4 100706 University of Alabama in Huntsville public Huntsville AL Southeast # 3 100690 Amridge University private Montgomery AL Southeast # 2 100663 University of Alabama at Birmingham public Birmingham AL Southeast # 1 100654 Alabama A & M University public Normal AL Southeast To get a feel for what data are available, look at the first six rows head(colleges) # unitid college type city state region #install.packages("dplyr") library(dplyr)ĭata: The file college2015.csv contains information on predominantly bachelor’s-degree granting institutions from 2015 that might be of interest to a college applicant. To begin, let’s make sure that our data set and the dplyr package are loaded colleges <- read.csv( "")
#Dplyr summarize ignore na how to#
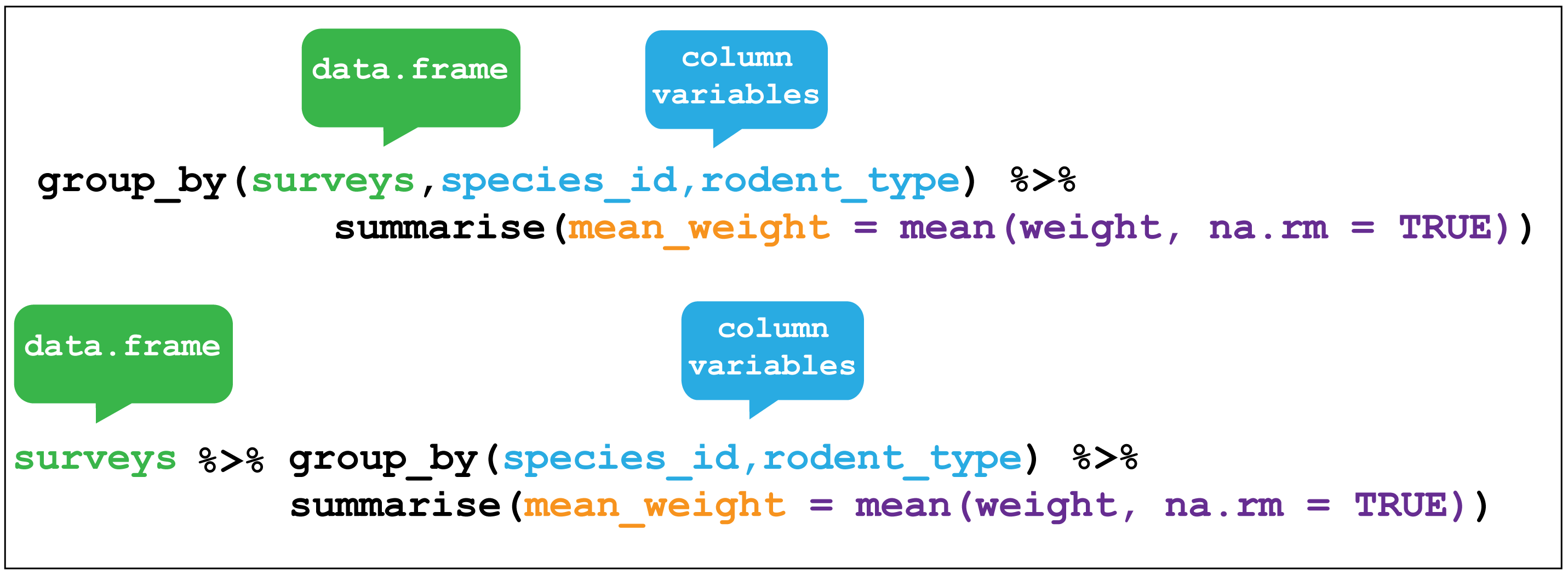
In this example we will explore how to use each of these functions, as well as how to combine them with the group_by function for groupwise manipulations. Pick variables by their names (i.e. specific columns)Īdd new calculated columns to a data frame Pick specific observations (i.e. specific rows) The core functions of the dplyr package can be thought of as verbs for data manipulation. The dplyr package contains a suite of functions to make data manipulation easier. Also learned how to calculate the median of a DataFrame column and Vector.Data manipulation is central to data analysis and is often the most time consuming portion of an analysis. In this article, you have learned what is median value and how to get it in R. The following examples demonstrate calculating the median when you have an even count and odd count of vector and also when you have NA values.

Similarly, let’s also calculate the median from the values of Vector.
On our DataFrame, we have a column price that has NA values. Let’s calculate the median on the column that has NA values by using the na.rm param to ignore NA values. The following example demonstrates getting median with and with out NA values on a column.Ĭalculating the median on a column that has NA values results in NA, you need to ignore the NA to get the right result. R Median of DataFrame Columnīy using R base function median() let’s calculate the median value of the DataFrame column.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
